end tidal co2 range in cardiac arrest
A prospective observational study. Here are five things you should know about waveform capnography in cardiac arrest.
Data from this prospective clinical trial indicate that findings from end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring during cardiopulmonary resuscitation are correlated with resuscitation from and survival of cardiac arrest.

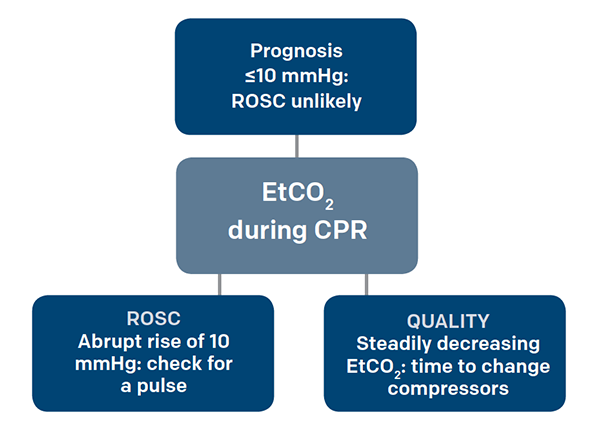
. Kolar M Krizmaric M Klemen P Grmec S. After 20 minutes of CPR death occurs if ETCO2 is consistently below 10 mmHg with 100 sensitivity and specificity 15. EtCO2 represents the amount of carbon dioxide at the end of exhalation.
Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed. Feb 6 2019. Guides chest compression quality persistently 20 helps identify ROSC sudden increase to 40.
Bobrow MD Daniel W. Successful resuscitation will show an increase in end tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2. Graphically this difference in ROSC vs non-ROSC PetCO2 for both groups appeared to be even greater at ten minutes.
The purpose of this systematic review is to evaluate the prognostic value of ETCO2 during cardiac arrest and to explore whether ETCO2 values could be utilised as a tool to predict the outcome of resuscitation. Capnography however reflects both a number EtCO2 in mm Hg and a waveform. Primary service area of an advanced life support ALS ambulance service including a city with a population of 70745 and the.
No patient with an average end-tidal carbon dioxide partial pressure of less than 10 mm Hg was resuscitated. End-tidal carbon dioxide cannot be used to rule out severe injury in patients meeting the criteria. Predicting ROSC from initial ETCO 2 cut-off value of 133 kPa had relatively wide range of sensitivities between 40 and 100 and.
A prospective observational study using a convenience sample. Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. Pierre Kory Laura OBrien RN CNS.
Association between Prehospital CPR Quality and End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide Levels in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Prehospital Emergency Care DOI. A critical tool in cardiac arrest. A prospective observational study.
Helps confirm tube placement. The dynamic pattern of end-tidal carbon dioxide during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Patients with lung disease and a larger etCO2-PaCO2 gap may have a somewhat higher PaCO2.
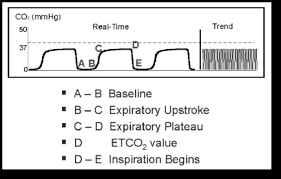
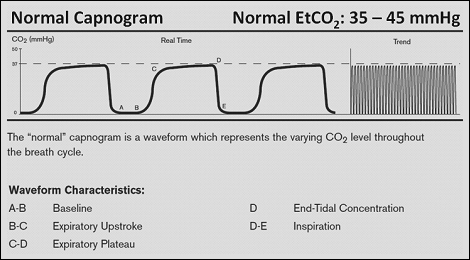
Remember a normal end-tidal is between 35 and 45. Capnography waveforms etCO2 and breathing patterns. PetCO 2 monitoring has been useful in determining the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
End tidal carbon dioxide CO2 correlates with cardiac output during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in cardiac arrest patients. An urban and rural emergency medical services system in northwestern Washington state. Even patients in cardiac arrest should have an etCO2 waveform albeit with a low etCO2 value.
MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST Presentation for MSBI Nurses Prepared by Dr. CO2 will decrease prior to a cardiac arrest in patients that are intubated in an intensive care setting. Multiple monitoring options so you can choose what and how to monitor respiratory status.
Cardiac arrest and shock states diminish cardiac output and therefore decrease elimination of carbon dioxide CO 2 from the lungs. Capnography has been used extensively during cardiac arrest situations when there is a need to do cardiopulmonary resuscitation. To assess the prognostic value of initial end-tidal CO2 pressures PETCO2 during CPR in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest OHCA.
Cardiac Arrest Ryan A. Quantitative relationship between end-tidal carbon dioxide and CPR quality during both in-hospital and out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
In mmHg the PetCO2 values for those with and without ROSC after five minutes of CPR was. Ninety consecutive victims of. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition.
17 hours agoEnd-tidal CO2 monitoring. End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. 1031091090312720151115929 To link to.
Difference between asphyxial cardiac arrest and ventricular fibrillationpulseless ventricular tachycardia cardiac arrest. During cardiopulmonary reanimation CPR the. In recent years there has been an increased interest in the use of capnometry the noninvasive continuous measurement of partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide petCO 2 in expired air.
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement. Levine RL Wayne MA Miller CC. In clinical observational studies mean ETCO 2 levels.
Prehosp Emerg Care. Ad View a brochure to learn about end-tidal CO2 capnography. CO 2 levels were significantly lower in cardiac arrest patients when compared with hypotensive patients 1 2 3 and 4 hours prior to a cardiac arrest see Table 1CO 2 levels were significantly.
A unique aide-memoire for capnography interpretation during cardiac arrest. Increasing CO2 during CPR can also indicate the return of spontaneous circulation. 428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg.
Measurement of end-tidal expiratory pressure of carbon dioxide ETCO 2 using capnography provides a noninvasive estimate of cardiac output and organ perfusion during cardiac arrest and can therefore be used to monitor the quality of CPR and predict return of spontaneous circulation ROSC. For most patients the gap between etCO2 and PaCO2 will be 5-10 mm which will leave them at the higher end of this range eg a pH of 74. Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide successful predicts cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the field.
Normal minute ventilation about 200 mlkgmin for dogs and cats in. Utilization of end-tidal CO2 monitoring has many advantages in cardiac arrest care. An accurate early predictor of the outcome of resuscitation is needed.
423 20 mmHg versus 34 255 mmHg. Spaite MD Chengcheng Hu PhD Robyn McDannold MS Tyler F. Lah K Križmaric M Grmec S.
Difference in end-tidal CO 2 between asphyxia cardiac arrest and ventricular fibrillationpulseless ventricular tachycardia cardiac. Literature search was performed using Medline and EMBASE. Because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not.
CC rate was not a predictor of ETCO2 over the dynamic range of actual CC delivery. In one of largest studies to date of prehospital capnography in cardiac arrest an initial EtCO2 10 mmHg 13 kPa was associated with an almost five-fold higher rate of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC. Mean CO 2 values were significantly higher in normal patients when compared with those in patients who had a cardiac arrest 3018 493 vs.
End-Tidal CO2 in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. The prognostic value of end tidal carbon dioxide during cardiac arrest. In addition a decrease in the EtCO2 during resuscitative events of 25 was associated with a significant increase in mortality independent.
In ventilation rate ETCO2 was lowered by 30mmHg p. End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 measurement can be used to predict death in prehospital cardiac arrest patients with pulseless electrical activity PEA. Murphy MD Bentley J.
BackgroundPhysiology 2 Monitoring end-tidal CO 2 ET-CO 2 provides instantaneous information about ventilation how effectively CO. Studies have shown that in patients who had ETCO2 of 10 mmHg or less cardiac arrest was associated with death 13 14.

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Sar Helicopter Paramedic Practice Etco2 Measuring To Assist With Cpr Attempts Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Potential Applications Of Capnography In The Prehospital Setting Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

End Tidal Capnography Can Be Useful For Detecting Diabetic Ketoacidosis Monitoring Copd Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Capnogram R Series Defibrillator Zoll Medical Uk

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project